
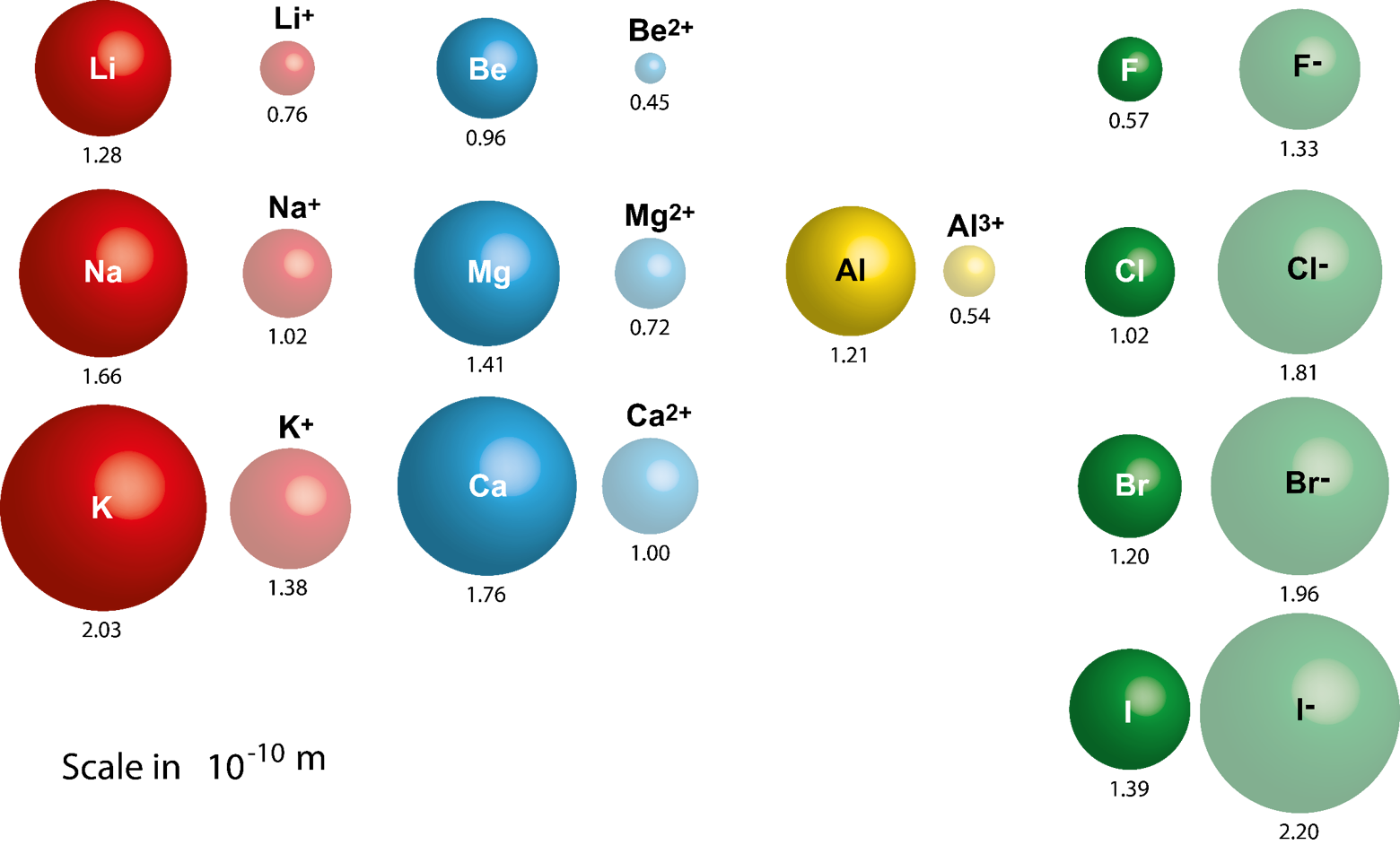

Down the period, however, the number of protons also increases. This is mainly due to effective nuclear charge. This is because while the number of electrons increases down the period, they only add to the same main energy level, and therefore do not expand the electron cloud. Atomic radius generally decreases from left to right across a period.That is, the further down a column, the greater probability of finding the outer electrons further from the atom, making the atom thus larger. This is a result of the increase in the principal quantum number, n. Atomic radius generally increases from top to bottom down a group.What are the general trends in atomic radii? We can then use these values to estimate bond lengths between different elements in molecules. So, if the bond between two Cl atoms in Cl 2 is 1.99 angstroms, we report chlorine's bonding atomic radius as about 0.99 angstroms.
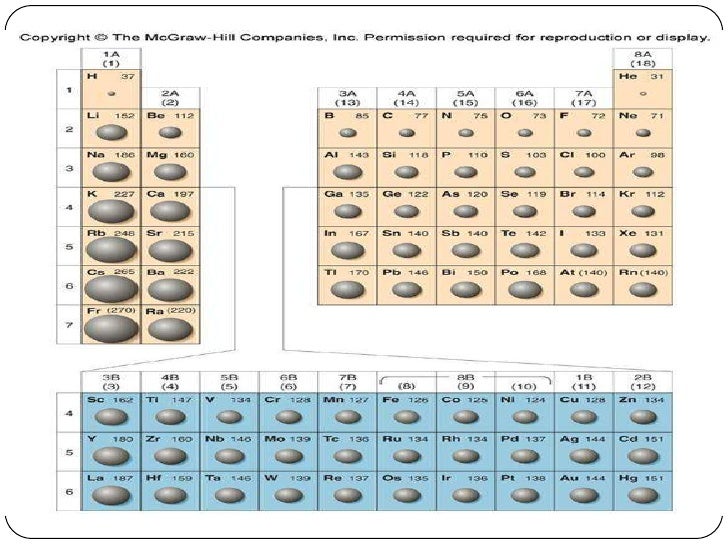
These are the radii of atoms that are chemically bonded to one another. Nonbonding atoms have a larger, more undefined or "fuzzy" radius, so when atomic radius is discussed as a periodic trend, what's usually meant is bonding atomic radius. Atomic radii are simply the radii (or half the "width") of these spherical atoms.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
